How to improve test cases
Tests serve a variety of purposes.
- Validate a feature does what it is supposed to.
- Validate changes to a feature do not break its expected supported usage.
But there are some additional things you can write in your test cases that may be useful.
- Validate a feature fails gracefully when given invalid inputs.
- Validate a feature works, even when given as many edge-cases as possible, as opposed to "common" input data.
How can you quickly tell what circumstances are covered by test cases though? The obvious option is to read the test cases and figure that out yourself. Ideally, the names of tests are descriptive enough to limit the amount of required reading for that. But there are additional options such as looking at test coverage and checking for branches that are not covered by tests.
Checking code coverage
You can check what branches in the source are covered by running the tests via gradlew test and then build the coverage report via gradlew buildJacocoAggregate. All tests are configured to log coverage data via JaCoCo, and the buildJacocoAggregate task generates a report consolidating coverage from all tests in all modules into a single report. You can access the report in ./build/aggregate/.
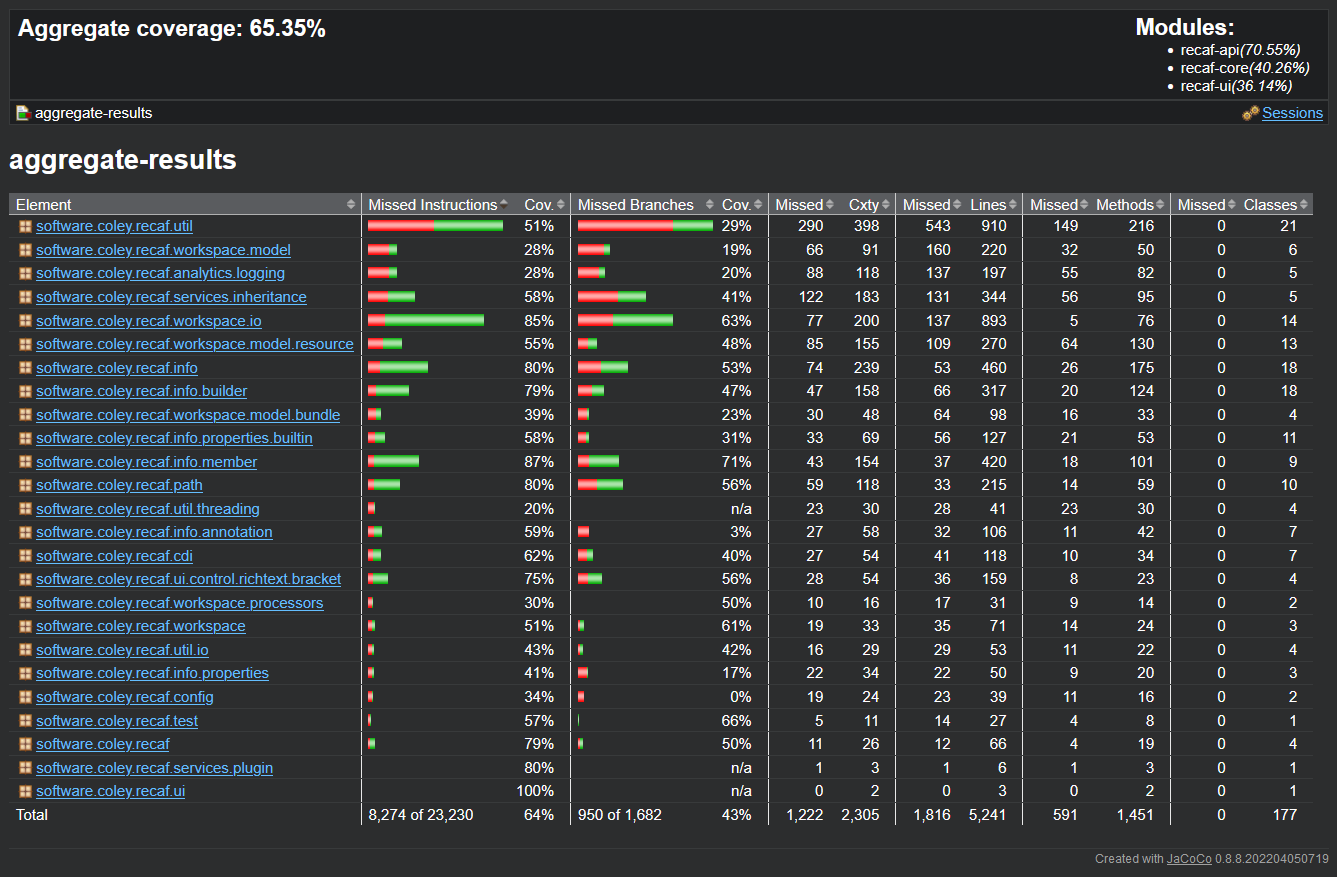
The main index page of the report shows a table of package's coverage
The main index page in the HTML report is a table showing which packages have the best code coverage. You can click on the packages to get data on each class in the package.
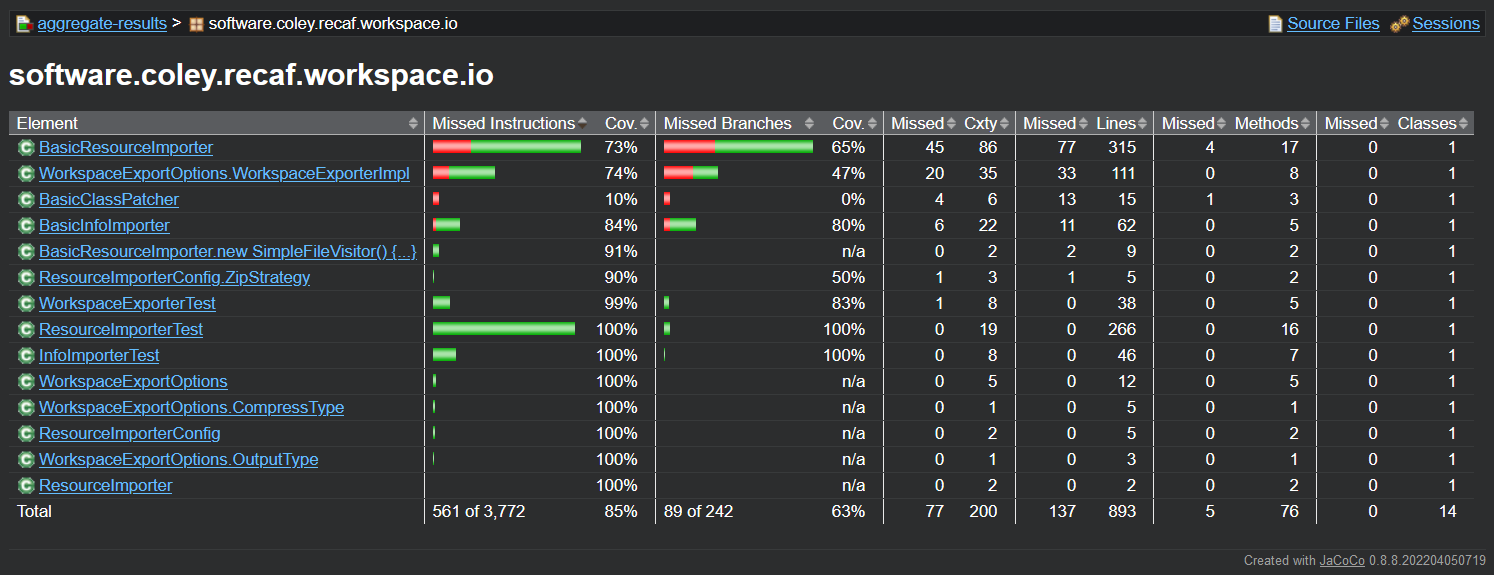
The table of a package's coverage shows per-class stats
Clicking on a class shows per-method coverage.
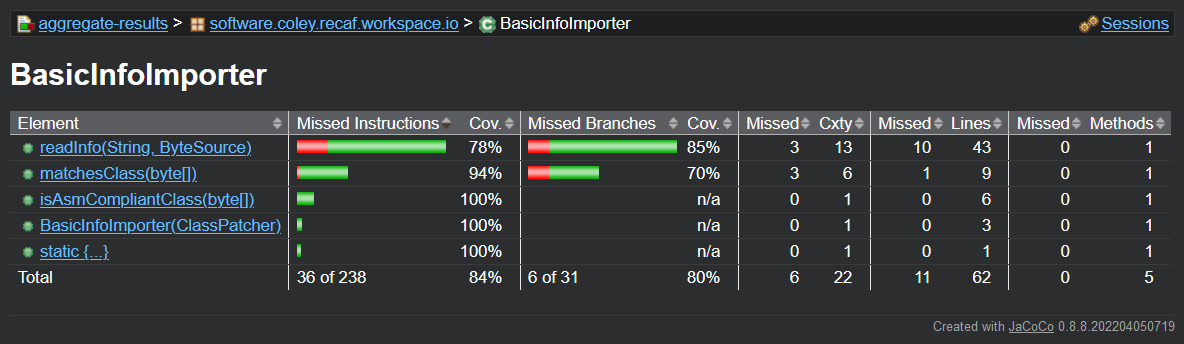
The table of a class's coverage shows per-method stats
Clicking on a method finally shows you the actual class source code, with information on coverage showed as line indicators. Clicking/hovering on them will reveal information like "1 out of 2 branches covered".
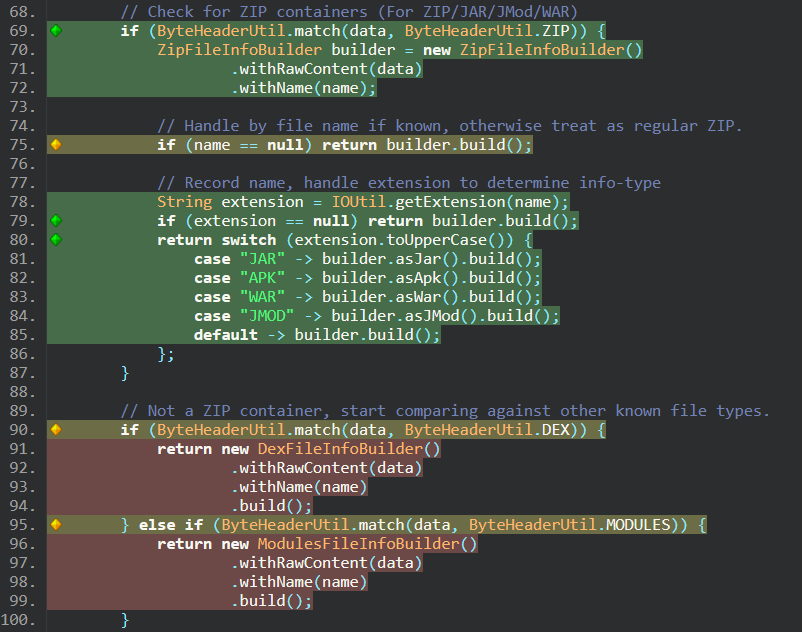
Green means all branches are covered. Yellow means some were covered. Red means the code was missed.
Naturally the more code that is covered the better. So using these reports to figure out where coverage is missing from really helps.
Why not use the built-in IntelliJ code-coverage feature when running unit tests?
Unfortunately, IntelliJ's code coverage support refuses to run if you attempt to run tests across multiple modules. Its been an open ticket since 2022 with no observed movement. You can use it if you test one module like recaf-core then another such as recaf-ui one after another, but you cannot combine those results together. If you just want to improve coverage over the recaf-core module then this is not an issue and you can use it to get accurate coverage data shown inline in the IDE.
Running a single module's tests in IntelliJ with code-coverage enabled.
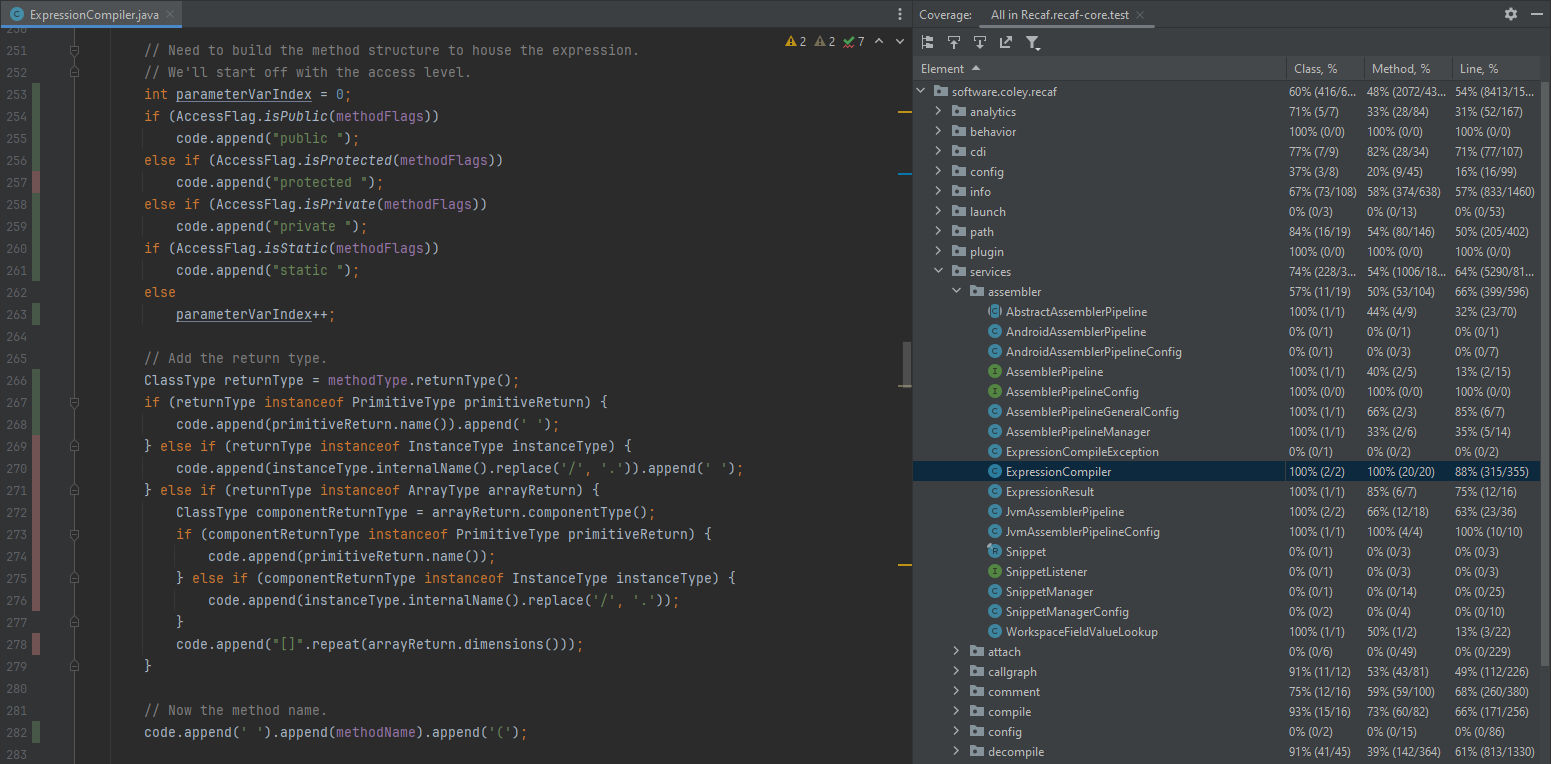
The results of running tests with code-coverage show a table of packages/classes and how much of the methods/lines are covered. In the code display, lines are colored to show which have been fully covered, partially covered, and completely missed during the test execution.
Checking code coverage online
If you want to see the current code coverage statistics and color-coded source without running the tests locally you can check out the latest codecov.io/Col-E/Recaf report. Do note that the way that CodeCov measures is slightly different than how JaCoCo measures coverage so the numbers may not match, but should generally be in the same ballpark.
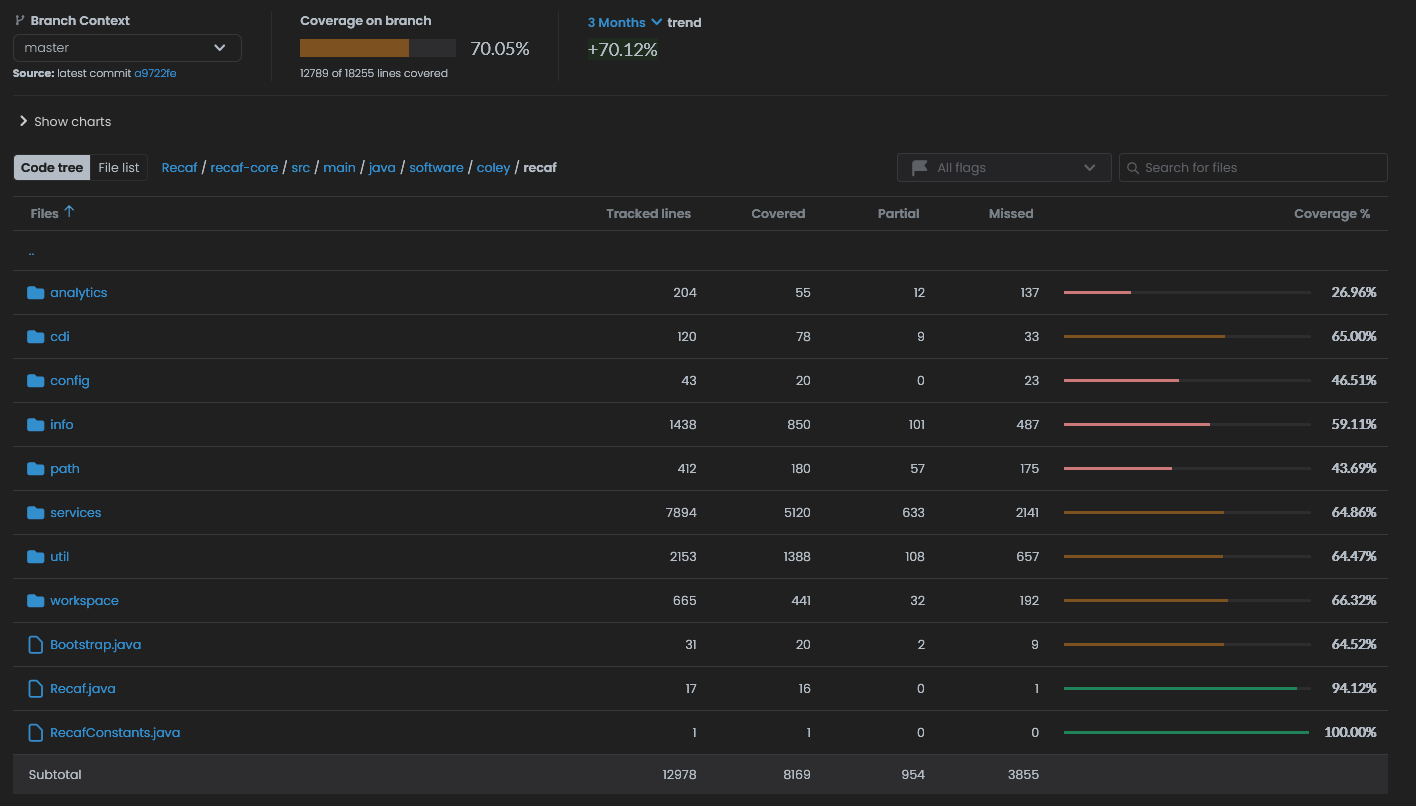
Screenshot of the code-coverage summary from October 2024. Recaf has a reported average of 70% code coverage across the project.